Effect of Active Learning Professional Development Training on College Student Outcomes
Is there an effect of participating in Active Learning Professional Development (ALPD) training on student performance?
Students who took a course with an ALPD instructor were three percentage points more likely to take additional classes in the same subject area compared to students who were taught by non-participant. Non-participants persisted at a rate of about 68%, so a three percentage point increase represents a 5% improvement. Importantly, ALPD training is related to higher likelihood of implementing active learning instructional practices in the classroom. We do not find any differences in students’ current course grade or performance in the next class.
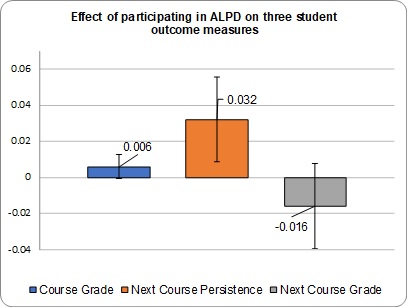
How to read this chart: This figure shows that students who took a course with an ALPD trained instructor were three percentage points more likely to take another course in the same field of study in the immediate next term (p<0.05). No clear difference in course grades was evident either in the ALPD-instructed course, or in the next course taken.
