Can nudging mentors weaken student support? Experimental evidence from a virtual communication intervention
Does reminding mentors to reach out support virtual communication?
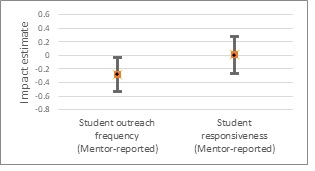
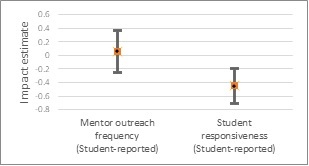
Not necessarily. This study tested the effect of a low-cost, light-touch intervention—mentor reminders—designed to bolster virtual outreach. The study examined impacts on the frequency of student-mentor communication and subsequent impacts on mentoring relationship quality. Unexpectedly, although students did not report receiving more (or less) outreach from mentors who received reminders, compared to mentors that did not receive reminders, treated mentors reported that their students initiated less outreach. In addition, students of treated mentors reported that they were less likely to respond to messages their received from their mentors.